Every day people from different countries keep emailing me asking me to help them with network penetration on how to create settings that allow them to browse for free without spending a dime.
Creating the configurations is not the problem; the problem arises when the person requesting the configuration does not understand simple terms like proxy, tunneler, port and all the rest.
Most of the time it is easier to send the person the tools needed to create that configuration, but when the person has little or no knowledge of these "free internet hacking terms" it becomes difficult to help.
Today I decided to create this post to explain the basic and popular terms that are related or have something to do with creating or testing free internet cheats on your network. If you want to learn or help your internet service providers look for loopholes in their network then I think this post will definitely help you, at the very least, it will help you get to know the basic terms. There are other tutorials I've made that would teach you how to easily create free internet setups that grant you free internet access. It is important that you know that the terms listed in this publication are not everything; these are the ones that came to my mind when writing this post. I'll add more to the list later.
Note: This post is for educational purposes only. Eugine Tech publishes these types of posts only to alert ISPs of their vulnerabilities. Applying or using this tutorial means you are O.Y.O (alone).
Free Internet Trick:
Free internet hacking refers to any setting or setting you apply on your device to access the internet for free without having to pay or subscribe to your internet service provider (ISP). Click here to view a list of free internet hacks.
Free Internet Tweak:
Some people mistake it for a free internet tricks. Free internet tweak refers to any trick that requires a "modification" to work. Some free internet tweaks are absolutely free, while others require a subscription package to work. Examples of settings that require a subscription to work are Blackberry subscription, WhatsApp subscription, Facebook subscription, etc.
Let me use the Blackberry subscription and explain how it works. Blackberry subscription is designed for Blackberry devices only, but you can adjust or change it to work on other devices such as Android, iPhone and PC. What is the benefit of using a Blackberry subscription? Blackberry subscriptions are much cheaper than others and at the same time offer unlimited internet access (most of them) because Blackberry compresses and uses less data. An Android device can use 1GB of data to download a movie, while a Blackberry device can only use 400MB or less to download the same movie. The bad part is that an Android subscriber pays more for data than BB users. An Android user could pay $ 30 for 6GB of data, while a BB user could pay $ 20 for unlimited internet access. Click here to visit Blackberry Free Internet Settings!
ISP:
ISP stands for Internet Service Provider. These are the companies that provide Internet services. Examples of these are MTN, Airtel, Vodacom, Telenor, Etisalat, Orange, Safaricom, At & T, etc.
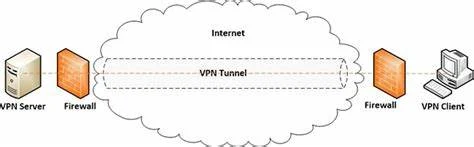
Tunneler:
These are applications that funnel our Internet connection through a secret tunnel to hide our online activities from our ISPs.
In this post, tunnelers are used to bypass our ISP's firewall and give you free internet access. Powered with the correct settings, these tunnellers would easily force an injection and then funnel their activities through a private tunnel on your ISP's network so they don't notice your traffic and block your connection.
If you are thinking about tunnellers, then you are thinking about VPN, SSH or something else. VPN and SSH tunnelers work in a similar way.
So what's the difference?
There are some notable differences between a VPN and an SSH tunneller. Here are just a few.
Speed - A VPN connection always tends to be faster than SSH, although it doesn't always happen. However, a VPN always seems to have an advantage over SSH in terms of connection speeds. But make no mistake, this comparison doesn't mean your SSH is slow.
More secure settings state: Your free internet settings have a better chance of lasting longer on your SSH than your VPN. On a scale of 1 to 100, VPN appears to receive more than 80% attention than SSH. Everyone wants to use a VPN, everyone wants to edit, and everyone wants to edit, even a 12-year-old can freely edit a VPN and add a shitty controller option to it. Most of these VPNs offer a small level of anonymity that easily exposes your configuration settings.
Examples of VPN tunnelers are Psiphon driver, Finch VPN, Droid VPN, Netloop, Your-Freedom, etc., while SSH is an HTTP injector, eProxy and the rest.
IP:
This stands for "Internet Protocol" and is the standard that allows different devices running on different platforms to communicate with each other. Here is the definition of the laity. An IP address could be called an address linked to each computer where they use it to communicate and identify themselves. When we browse the web, our IP address reveals details about us, details such as our country, the device we are using, the operating system and many other things.
Some people don't like to expose their data, so they use the service of a proxy or a VPN to ensure their anonymity.
Proxy:
Now I would like you to pay attention here and not get confused. A proxy is an IP address, but it is used to represent the original IP of a device or other devices. People use proxies for several reasons. Some use it to hide or cover their original IP address, others use it to bypass geo-restriction on the web and many other reasons. There are different types of proxies, such as anonymous proxy, Squid proxy, transparent proxy, CGI proxy, distortion proxy, etc.
Proxy server:
I thought you read what a proxy is and figured it out. So what is a proxy server?
In this post, a proxy server is a means through which all computers on a network must go through to access the Internet. You use your ISP's proxy server to access the Internet and then your ISP can monitor it and filter what it wants you to access. When you run out of data, your ISP proxy server will easily block your connection and won't allow you to access the internet because it has been programmed to only allow you to access the internet when it has data.
Well, just because your ISP proxy server is refusing your connection doesn't mean you can't browse for free. These proxy servers are simply programmed to block all your internet connections, but they allow you to access certain websites like the free pages I mentioned above. You have two ways to access the internet, either by bypassing your ISP's firewall or by getting another proxy server that allows you unlimited internet access for free.
There are many ways to get a working proxy server that easily gives you free internet access on your ISP's network. It is important to know that these proxy servers are not just common.
Ports:
A port is a medium or portal where information is sent back and forth between the computer and other networks. We need ports to browse the web and therefore we can also use open ports on our ISP network to browse for free. Let's take a house as an example. To access a house, we would need the doors or windows, so when the homeowner closes the doors and windows, we will not be able to access the house unless we look for another open door or window. The home in this scenario is the Internet, while the doors and windows are the ports. Once your internet service provider (ISP) closes them, you won't be able to access the internet.
Your ISP can never close all ports on your network, so you can search for open hidden ports and use them to access the internet for free. Some people rely solely on open ports like UDP and TCP to create free internet access settings. Below are some of the ones I would talk about.
UDP port: They are very fast and if they are open on a network, they can be browsed directly for free, i.e. you can search for open ports on your network and if there are any you can use them to browse for free. Examples of such gates are 53, 9201, 9200, etc.
TCP port: they are fast but not up to UDP. TCP ports should now not be considered ineffective due to their comparison to UDP ports. In my other posts, I have given this formula for free Internet access; Open Ports Proxy Host Working = Free Internet!
Ping:
Pinging simply means making a query or request over a network to determine if there is a connection. The purpose of pinging is to make sure that you can establish a connection between you and your destination. There are so many ways that pinging a request on your ISP's network can go a long way in getting free internet, I'll leave a tutorial to walk you through this soon.
Data packets:
Data packets or packets refers to the amount of data that is sent to the computer over a network. The data sent can be over the Internet or any other packet-switched network.
What do you think of the list above? Please comment on anything you believe is missing.





.jpg)



